NorComp's highly reliable telematics connectors offer IP67/IP68 moisture protection, high mating cycles, and excellent performance in high vibration environments. Applications such as emergency warning system for vehicles, GPS navigation, vehicle tracking and fleet management devices all require a secure, reliable connection critical for the precision of the telematics technology reporting. Our connector family offers a variety of solutions to the challenges encountered in ruggedized telematics applications. To help you choose from our wide array of connectors with Telematics applications, we've broken down the functions and systems along with highlighting the best fits from our many product lines.
Table of Contents
- WHAT FUNCTIONS DOES A TELEMATICS SYSTEM PERFORM?
- WHAT ARE SOME TELEMATICS APPLICATIONS?
- CONNECTORS FOR TELEMATICS APPLICATIONS
- GUIDELINES FOR CHOOSING A TELEMATICS CONNECTOR
- TOP NORCOMP CONNECTORS RECOMMENDED FOR TELEMATICS APPLICATIONS
- CUSTOM CONNECTORS
- RESOURCES
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field that involves data collection for cars, trucks, equipment, and other mobile assets. It is a method of monitoring movements and logging system parameters with GPS and on-board diagnostics (OBD). Telematics is an essential management tool for many commercial and government fleets and is being adopted in many non-transport industries.
This page discusses the characteristics of a telematics application, and the challenges they pose to telematics connectors. It then reviews the recommended solutions for telematics applications and concludes with a list of recommended resources for designers.
What Functions Does a Telematics System Perform?
Businesses use telematics in the areas of safety, productivity, regulatory compliance, sustainability, optimization, and more. As the technology becomes less expensive and easier to use, more businesses are incorporating telematics into their everyday operations.
In some cases, telematics has already been adopted under another name. For example, eCall (“emergency call”) is an initiative by the European Union that incorporates telematics as a standard feature in new vehicles. It is intended to bring rapid assistance to motorists involved in a collision anywhere within the EU. A vehicle with eCall can automatically contact emergency services after a serious accident, sending the location, plus airbag and crash sensor information. eCall was made mandatory in all new cars sold within the European Union after April 2018 and other countries have begun to adopt similar systems.
Ongoing work on V2X standards will take these capabilities to a new level, enabling vehicles to communicate in real time with each other, the surrounding infrastructure, and even pedestrians. Once implemented, a connected vehicle will provide real-time data on location, speed, and other parameters with the goal of reducing accidents.
In general, telematics designs range from basic systems that meet the minimum electronic logging regulatory requirements, to comprehensive fleet or logistics management platforms that provide numerous additional functions.
A basic telematics system typically contains a GPS device, a data logger, a wireless connection such as a cellular modem, and a backup battery. A vehicle application will also include an engine interface.
An advanced telematics system can include additional hardware or software capability such as:
- Additional communications: options such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enable data access through a smartphone app or WLAN
- Safety-related options: seat belt monitoring, cameras, distraction monitoring, and weather hazard alerts
- Productivity options: electronic logging, geofencing, asset tracking, trip history logging
- Platform functions: data integration, mobile integration
- Regulatory compliance: temperature monitoring, driver time logging, vehicle inspection monitoring, emissions-related logging
- Optimization options: fuel consumption, remote diagnostics, fault detection, route optimization, idling trends
Many of these functions have a cloud-based component, too. Customers can send the data gathered from multiple units to the cloud to provide data for longer-term programs such as business planning and cost analysis.
What are Some Telematics Applications?
Applications for telematics in vehicles include onboard diagnostics (OBD), emergency warning systems, GPS navigation, and vehicle tracking; non-vehicular applications include shipping container tracking, real-time data collection, asset tracking, and logistics.
Telematics offers many advantages for vehicle fleet operators, helping them save time and money. Tracking work trucks on their daily routes is one example. Electronically monitoring fuel usage and mileage is another. Some other application use cases are:
Regulatory compliance. Telematics can help truckers, dispatchers, and business owners comply with the various regulations that govern commercial trucking. For example, the US Department of Transportation regulates the number of hours a truck driver may work per day and per week. Similar restrictions are in place for drivers who transport passengers.
Route optimization. Inefficient routing wastes time and resources. Telematics can provide insights to optimize driver routing to save time and fuel: for example, by choosing drivers based on their proximity to customer sites.
Monitoring idling performance. Excessive idling can waste fuel and increase engine wear. Telematics can indicate when a vehicle is idling and can also distinguish between working idle time—which is needed to operate equipment or cool off the cab, for example—and idling without a work-related purpose.
Predictive maintenance. In a large commercial fleet, it can be hard to track vehicle maintenance schedules for routine items such as oil changes, brake service, and tire rotations. Neglecting these items can reduce vehicle operating life, cause a breakdown, or even increase the risk of an accident. Telematics can eliminate guesswork, allowing the operator to track vehicle operation and schedule maintenance at predetermined intervals.
Safety. Telematics can help reduce speeding, curb harsh driving, and encourage seatbelt use. In-cab cameras can monitor behavior to detect distracted or sleepy drivers.
Telematics is widely used in non-vehicle applications, too.
Equipment tracking. The theft of a piece of heavy equipment can cost its owner hundreds of thousands of dollars. Telematics can track this equipment at all times and can even help locate missing items on a job site or checking that they are returned after use. A telematic system can also allow for geofencing—establishing a virtual perimeter to restrict operation to a defined area.
Container tracking. Logistics managers in the shipping industry must track thousands of containers as they proceed to their final destinations. Managers of railroad freight operations have similar requirements. A smart container adds telematics to monitor status and location, as well as parameters such as door status (open/close), and environmental conditions such as temperature, shock, and vibration.
Even small containers can benefit from the addition of telematics. For example, a vaccine can lose its effectiveness if it exceeds the safe storage temperature. Real-time monitoring of a shipment can ensure that the vaccine always remains within the allowable temperature range.
Railroad telematics. Telematics applications for railroads include automatic stock control, estimated time of arrival (ETA) management, railcar tracking & tracing, refrigerated wagon management, remote data access, shock detection, and others.
Telematics in aviation. Although normally discussed in terms of automotive or freight logistics applications, telematics systems can also be used in aviation, especially to improve the efficiency of ground handling operations. Telematics provides many of the same services used in vehicle and freight operations, including asset tracking, geofencing, fuel consumption optimization, and cloud-based management.
Connectors for Telematics Applications
Although an OEM installation may be integrated into the vehicle wiring harness and have few, if any, connectors, an aftermarket installation or standalone module will require an enclosure, cabling and connectors. Connectors for telematics applications must maintain a secure, reliable connection while operating in a harsh environment that includes extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, and the presence of liquids.
Very rugged systems will place multiple requirements on the board and connectors, specifically when environmental conditions are considered. In a rugged telematics systems design, connectors play an important role in determining reliability.
There are several options for telematics connectors, depending on whether data or power are needed at the system interface. Telematics connectors share some similar electrical and mechanical characteristics. In a fleet application connectors interface with the vehicle through its onboard diagnostics (OBDII) port or via another in-vehicle port such as Controller Area Network (CAN) bus.
Inside a telematics system, there will be a PCB with multiple connectors to provide data and power connections to the internal systems within a vehicle. Connectors may be board-mounted or chassis mounted and will connect to the PCB with a short cable. The connectors form an interface with the external environment, so rugged telematics connectors may be needed if environmental exposure poses a danger to system operation.
Guidelines for Choosing a Telematics Connector
Except for specific form factors such as an automobile OBDII port, the connectors used to interface with a telematics system are not standardized. The initial considerations are pin count and footprint. The operating environment is important for connector selection, too.
In a vehicle, telematics equipment may be installed in a passenger compartment or other protected location. Alternatively, it may reside under the hood where it is exposed to a range of undesirable conditions such as extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, corrosive liquids, high humidity, and so on. A telematics application in a shipping or railroad application can also be exposed to harsh environment conditions.
Deployment in harsh environments places important design requirements on rugged telematics connectors. The IP (Ingress Protection) rating of a connector is an important parameter. Defined by IEC standard 60529, the IP rating is used to characterize the resistance of connectors and electrical enclosures to dust or moisture. The corresponding European Union (EU) standard is EN 60529.
IEC 60529 provides users specific information about a connector’s performance. An IP rating has 2 digits after the IP, e.g., IP68. The first digit refers to protection against intrusion from solids and the second digit refers to protection against intrusion from liquids.
Solid intrusion ratings range from 0 (no protection against intrusion) to 6 (complete protection against dust ingress). Liquid intrusion ratings range from 0 (no protection against intrusion) to 8 (protection against long-term immersion to a specific pressure). There is also a level IP69K that signifies protection against steam-jet cleaning.
Each of the solid and liquid levels has a specific level of protection; a rating of IP67/IP68 is required for most telematics applications. NorComp offers several families of connectors that combine IP67/IP68 ratings with standard form factors.
Another important consideration is the number of make/break cycles that are expected. If the telematics equipment will be disconnected frequently, the maximum number of mating cycles and the ease of connection/disconnection becomes a factor.
Other design considerations are:
- Mechanical ratings, specifically shock/vibration resistance
- Power handling, specifically current/voltage ratings for power cable connectors
- Retention and keying mechanism, as well as the pulling force rating
- Operating temperature range or thermal cycling/shock limitations
Which NorComp Connectors are Recommended for Telematics Applications
Since most installations operate in harsh environments, NorComp recommends IP67 or IP68-rated connectors for telematics applications. The NorComp connector families recommended for telematics use are:
- VULCON™ Circular Connectors
- SEAL-D® waterproof D-Sub Connectors
- POWER-D& Combo-D Mixed D-Sub Connectors
- QUIK-LOQ™ Push-Pull Connector
The table below summarizes the IP ratings of these connector families.
|
Connector Family |
IP Rating |
|
VULCON™ M5/M8/M12 |
IP67/IP68 |
|
SEAL-D® |
IP67/IP68 |
|
POWER-D |
IP67 |
|
QUIK-LOQ™ 820K/821K/822K |
IP67/IP68 |
VULCON™ Metric Circular Connectors

The VULCON™ connector family conforms to the long-established industry-standard form factor for circular connectors with a screw fitting. The VULCON™ M-series connectors are rated to IP67/IP68 requirements.
The VULCON™ M12 circular connector has become a leader in telematics applications, as well as other harsh environment applications such as industrial automation, remote process sensors, robotics control systems, ruggedized networking, & power conditioning systems.
VULCON™ M12 connectors are now available in stainless-steel versions. These connectors provide upgraded corrosion resistance for the most rugged applications. M12 connectors are available in 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 8-, and 12-pin configurations with A, B, D, L, S, and X key coding options.
The VULCON™ M8 circular connector is a smaller more compact version of the M12. M8 connectors are used in applications requiring a rugged and robust fully shielded metal shell able to withstand shock and high vibration. M8 connectors are available in 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6-pin configurations with A or B key coding options.
VULCON™ M5 connectors are recommended for telematics applications that require the most compact connector solution. Other M5 connector applications include transportation and control systems, automated doors & ramps, and sensor connectivity. M5 connectors are available in 2-, 3-, or 5-pin configurations.
QUIK-LOQ™ Push-Pull Connectors

QUIK-LOQ™ Circular Push-Pull Connector systems are rugged, sealed connectors ideal for telematics applications where quick connect/disconnect and environmental protection are required.
There are several families of QUIK-LOQ™ connectors. Metal shell connectors are available with both IP67/IP68 ratings for harsh environments and IP50 ratings for less demanding environments. Metal shell connectors feature 360° shielding for full EMI / RFI protection. Plastic shell connectors are also available.
IP-Rated D-Sub Connectors
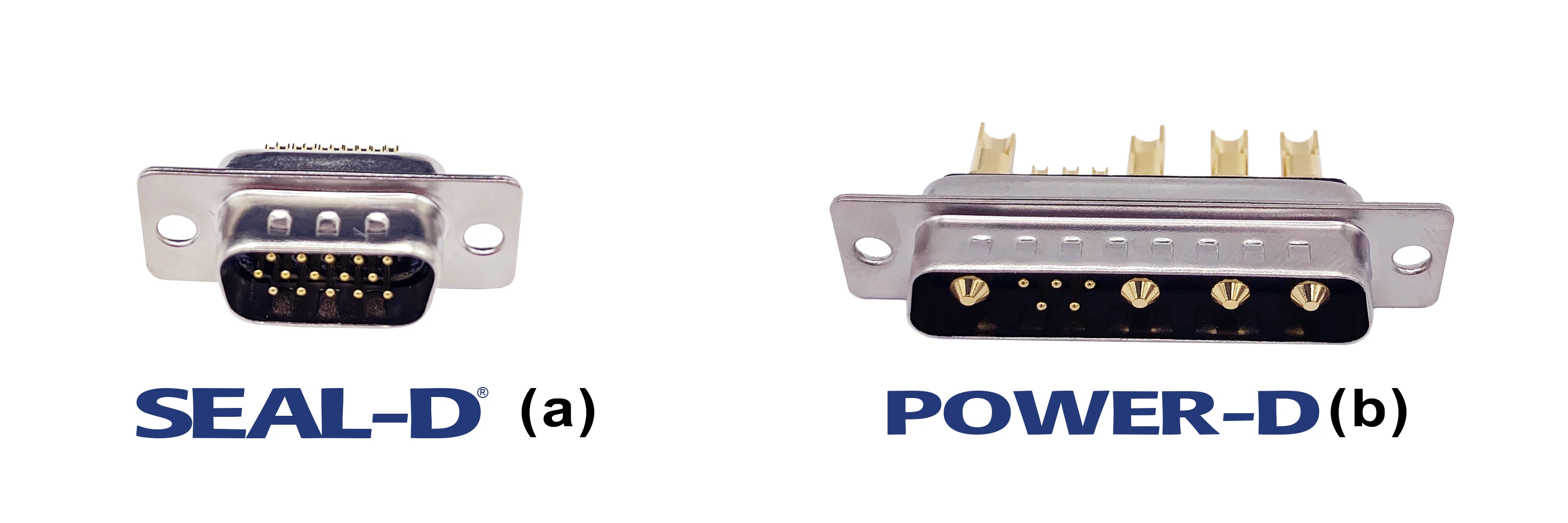
NorComp offers two families of d-sub connectors with IP ratings. SEAL-D® connectors are designed for telematics applications that require both the d-sub form factor plus IP67/IP68-rated protection from heavy spray or short-term submersion.
The SEAL-D® family are drop-in replacements for standard unsealed connectors. This eliminates the need to change PCB and sheet metal designs when upgrading to an IP-rated solution. They maintain the same footprint as the standard d-sub product offering but are sealed internally. NorComp’s proprietary sealing technology allows any existing d-sub product to be manufactured in an IP-rated version.
SEAL-D® connectors are available in vertical and right-angle board mount types as well as solder cup for panel mount cable applications.
Depending on where a telematics system is deployed, it may need both data and power connections in a single shell. POWER-D SEAL-D® connectors are designed for harsh environment telematics applications where both power & signal are required from a single connector. Featuring “Solid-Pin” machined contacts, these connectors offer high reliability performance for the most challenging design applications. The diverse product family features up to 12 industry-standard contact configurations. Features include:
- Signal/low power in 6 standard sizes (standard 9, 15, 24; high density 15,26.44)
- Combo-D/high power in a variety of configurations (3W3, 5W1, 7W2, 9W4, 11W1,13W3,13W6,17W2,21W1,21W4)
- Solder up, vertical mount, & right-angle board mount option
- High-reliability screw machined contacts
- 3 amp, 5 amp, 20 amp, and 40 amp power options
- -55 °C to +105 °C operating temperature range
Custom Connectors
Since there are so many possible configurations for a telematics application, an off-the-shelf solution may not always fit the bill. NorComp is well qualified as a design partner for custom connector and cable solutions. We can take any custom SEAL-D® connector or cable project from concept and prototyping to full volume production.
NorComp also manufactures custom circular connectors for many customers who require unique project design specifications for telematics and other demanding end-use applications. Contact us for more information.
Resources
The NorComp website has several resources for those wishing to learn more about the various types of connectors recommended for outdoor sensor applications. Resources include:
Rugged Environment Certified connectors
Transportation industry connectors
Environmental Compliance statements
White Papers: Custom project success stories
Click on the links or contact us for more information.
Related Products
Categories
- Circular Connectors & Cable Assemblies
- D-Sub Connectors
- IP67 D-Sub Connectors
- D-Sub Backshells
- Micro-D Connectors & Cable Assemblies
- Power-D & Combo Mixed Connectors
- Push Pull Connectors
- D-Sub & Micro D Hardware
- Modular RJ45 Connectors
- USB Connectors
- D-Sub Adapters & Gender Changers
- SCSI .085"/.050"
- .050 Ribbon
- Headers & Receptacles
- Bayonet Connectors








